Your thyroid, although small, plays a massive role in your overall health. It’s like the manager of your metabolism, influencing how your body uses energy.
Many clients come to me with thyroid issues, often detected through blood tests, including something known as “TSH reflex.”
Let’s break down what this means and how you can manage your thyroid health effectively.
What is TSH with Reflex to Free T4?
When we talk about “TSH with reflex to Free T4,” we’re getting into specific tests used to assess your thyroid function. Here’s what these terms mean:
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): This hormone tells your thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones (T4 and T3). An abnormal TSH level can suggest problems with your thyroid.
- Free T4: This refers to the unbound thyroxine in your blood, available for your body to use. It’s a direct measurement of the hormone your thyroid gland is producing.
The “reflex to Free T4” part means that if your TSH levels are off, the lab will automatically check your Free T4 levels to give more insight into what’s happening with your thyroid.
Understanding Your Thyroid Test Results
Thyroid Health
When you get your thyroid tested, you’re looking for a few specific markers:
- TSH Levels: The normal range for TSH is typically between 0.4 to 4.0 milliunits per liter (mU/L), but this can vary based on the laboratory’s specific reference range.
- Free T4 Levels: For adults, a normal Free T4 range is approximately 0.8 to 1.8 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL).
If your test results fall outside these ranges, it might indicate a thyroid issue requiring further investigation or management.
Common Thyroid Disorders
Various thyroid disorders can affect your health. Here are the most common types:
- Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid): Your thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms might include sweating, weight loss, anxiety, and a rapid heartbeat.
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid): If your thyroid isn’t making enough hormone, it can make you feel very tired, cause you to gain weight, and make you feel sad or depressed. This happens because the thyroid hormone helps control how your body uses energy. Without enough of it, everything slows down.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition where your immune system attacks the thyroid, often leading to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Cancer: There are different types of thyroid cancer, but many are treatable.
- Postpartum Thyroiditis: Some women develop thyroid issues after giving birth.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Thyroid Health
As a nutritionist, I always advocate for a holistic approach to health. Here are some lifestyle changes that can support your thyroid health:
Manage Stress
Stress can adversely affect your thyroid:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Activities like yoga, meditation, or simple breathing exercises can help manage stress.
- Ensure Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Optimize Your Diet
Your diet plays a crucial role in thyroid health:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a variety of nutrients. Include fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Limit Processed Foods: These can contribute to inflammation and worsen thyroid function.
- Be Mindful of Iodine: Your thyroid needs iodine to produce hormones. Include iodine-rich foods like fish and dairy, but don’t overdo it, especially if you have Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis.
Stay Active
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and manages symptoms:
- Incorporate Regular Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, like brisk walking or cycling.
Monitoring and Medication
While lifestyle changes are beneficial, they might not be enough on their own. You may still need:
- Regular Thyroid Testing: Keep track of your thyroid function with regular tests.
- Thyroid Medication: Some conditions require medication like levothyroxine, especially if you have hypothyroidism.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
It’s crucial to collaborate closely with your healthcare provider to manage your thyroid health:
- Discuss Your Test Results: Understanding your specific needs can help tailor your treatment.
- Adjust Medications as Needed: Your needs might change over time, and so might your medication dosage.
- Regular Follow-ups: Keep in touch with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
FAQs
What are the signs of a thyroid problem?
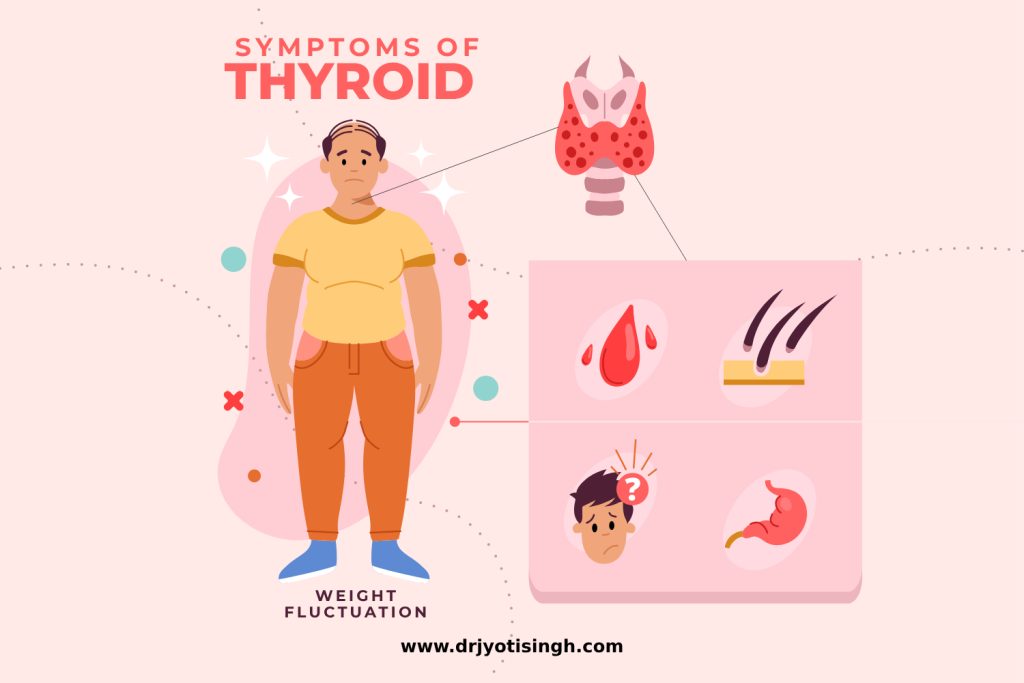
Common signs of a thyroid issue include unexpected weight changes, feeling unusually tired or anxious, changes in your heart rate, feeling too cold or too hot, and changes in your hair or skin texture.
How can I tell if my thyroid is underactive or overactive?
An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) usually causes symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and feeling cold. An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) might cause weight loss, nervousness, rapid heartbeat, and heat intolerance.
What is a TSH test and why do I need it?
A TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) test measures how much of this hormone is in your blood. It helps doctors understand how well your thyroid is working and if your thyroid medication needs adjustment.
Can diet affect my thyroid health?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in thyroid health. Nutrients like iodine, selenium, and zinc are crucial for thyroid function. However, it's important to balance these correctly, especially if you have thyroid conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Is thyroid disease permanent?
It depends on the type and cause of the thyroid disease. Some conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis are usually permanent and require ongoing treatment, whereas others, such as some cases of hyperthyroidism, can be temporary or managed effectively with medication.
Can I live a normal life with a thyroid condition?
Absolutely! With proper diagnosis, effective treatment, and regular monitoring, most people with thyroid conditions can lead normal, active lives.
Conclusion
Thyroid health is complex but manageable with the right approach.
By combining a healthy lifestyle with regular medical care, you can effectively manage your thyroid condition and improve your overall well-being. Remember, each person is unique, so what works for one might not work for another.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and work with your healthcare team to keep your thyroid—and your body—in good health.








